Table of Contents
A Catch-All (Default) Email Address: What Is It?
An email address that receives all incoming messages sent to any invalid or nonexistent mailbox on your domain is known as a catch-all email address, or default address in cPanel hosting.
For instance, if someone sends an email to john@example.com but that mailbox is empty, the email will be sent to the catch-all address rather than bouncing back.
Why Make Use of a Catch-All?
To ensure you don’t miss any email due to typos in mailbox names.
Useful for businesses where even misaddressed emails need to be collected.
Steps to Set Up a Catch‑All
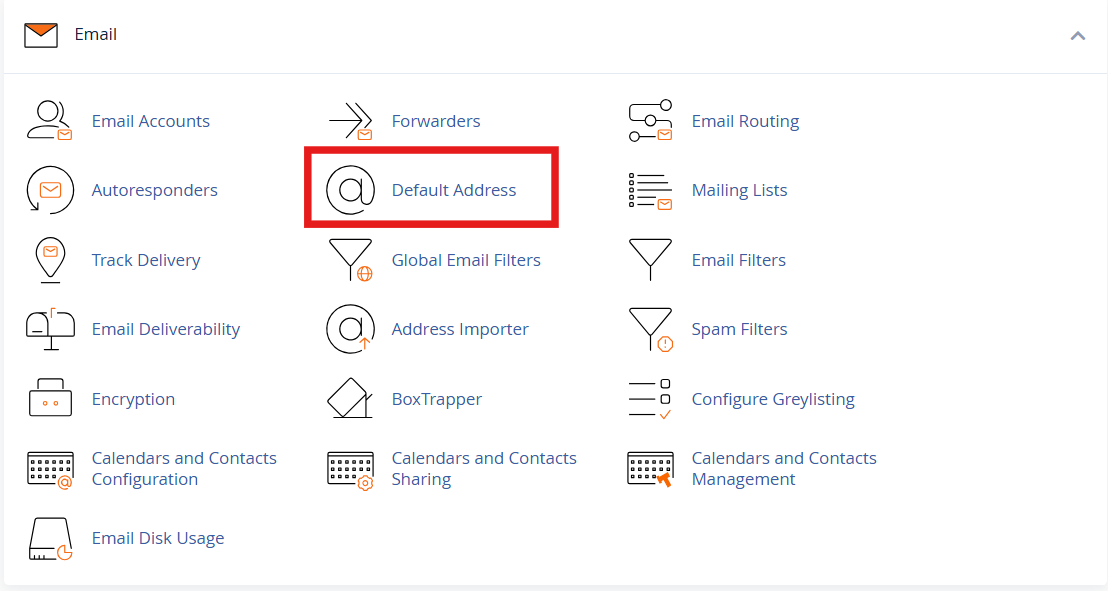
Log in to cPanel and go to the Email section, then select Default Address.
-
Choose the domain for which you want to enable the catch-all.
-
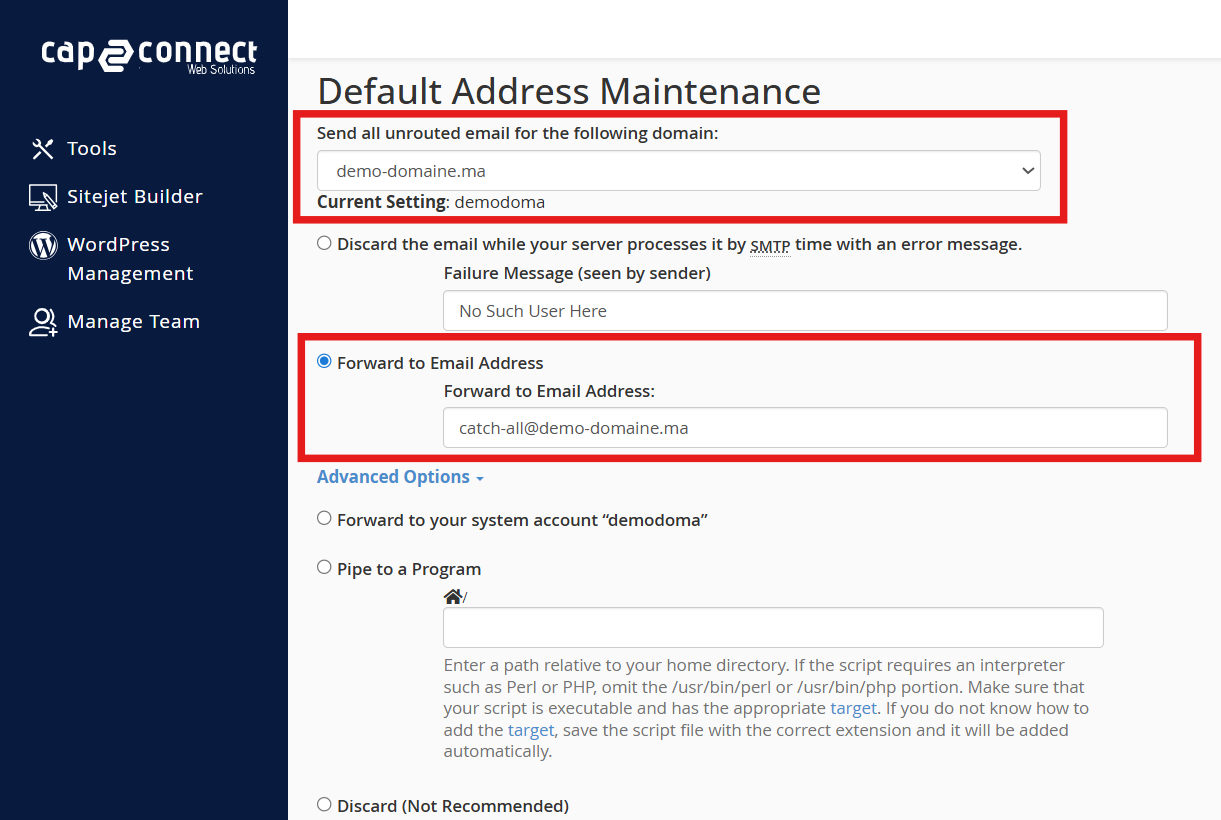
Decide how you want to handle emails to unknown addresses. The usual option is to forward them to a dedicated mailbox, like catch-all@example.com. Other options include bouncing the email back or discarding it silently.
-
Save the settings and test by sending an email to a non-existent address under your domain to confirm it arrives at the catch-all mailbox.
Risks and Downsides
Catch-all addresses have drawbacks, even though they can be very helpful for personal or business domains where you want to ensure that every email is received. Such as :
- Increased susceptibility to spam because catch-all addresses send emails to mailboxes that don’t exist.
- Possibly increased server load and disk space usage.
To keep your primary inbox organized, always use a separate mailbox for your catch-all emails. Catch-all addresses often draw unsolicited emails, so keep an eye on your mailbox and make sure your spam filters are turned on.
It might be wiser to turn off catch-all and set up specific forwarders for just the addresses you anticipate receiving emails from if the amount of spam gets too high or disk space starts to fill up.
A catch all email address is a simple but powerful tool to make sure you never miss emails, even if they’re sent to a wrong or non-existent address. With careful management and good spam protection, it can help keep your domain’s email communication reliable and organized.
Bottom line: Only use a catch‑all if you have a specific need and can manage the extra email volume.
Definitions
-
Unrouted email: Email sent to an address at your domain that does not exist.
-
Mailbox: A real email inbox (e.g., info@example.com).
-
Forwarder (alias): An address that automatically forwards email to one or more other addresses.
-
Bounce: When an email cannot be delivered and the sender receives a failure notification.
-
Pipe to a program: Advanced setting to forward emails to a script instead of a mailbox.
-
Dictionary attack: Spam method that targets multiple random mailbox names; catch‑alls are more vulnerable.