Using cPanel, you’ve probably noticed two interfaces for managing PHP version and options: EA-PHP (EasyApache PHP) and ALT-PHP (Alternative PHP). While both serve the same purpose (running PHP code), they are designed for different use cases.
EA-PHP is the official PHP package managed through EasyApache 4. Through EasyApache 4, you can manage the PHP versions of your hosting. EA-PHP integrates deeply with cPanel features like PHP-FPM, MultiPHP Manager, and Apache. It’s the standard and recommended PHP system for the majority of modern websites.
ALT-PHP, on the other hand, is provided by CloudLinux. It allows you to use much older PHP versions (down to PHP 4.4 or 5.2), which are no longer supported by the official PHP team. These versions are patched by CloudLinux to remain secure. ALT-PHP is managed through the PHP Selector tool in cPanel and offers users more control over extensions and configuration.
Table of Contents
Key Differences
The main difference is the range of PHP versions available. EA‑PHP provides current, actively supported PHP versions like PHP 8.1, 8.2, and 8.3. ALT‑PHP supports those versions too, but also includes older, legacy versions for websites that haven’t been updated to newer PHP.
Another big difference is how extensions are managed. With EA‑PHP, the server administrator enables or disables PHP extensions globally using EasyApache 4 or MultiPHP INI Editor. With ALT‑PHP, each individual cPanel user can go into PHP Selector and choose their own extensions—this is useful on shared hosting.
In terms of user control, EA‑PHP is mainly controlled by the server admin, while ALT‑PHP allows more flexibility for cPanel users. You can customize your PHP version and settings without needing WHM access.
Finally, performance and integration are smoother with EA‑PHP. It works well with PHP-FPM, Apache modules, and cPanel’s native tools. ALT‑PHP is better suited for websites that rely on older code or require specific legacy extensions.
Which One Should You Use?
If your website is running modern software like WordPress, Laravel, or other current frameworks, you should use EA‑PHP. It’s fast, secure, and fully integrated with cPanel tools.
If your site uses an old CMS or custom code that doesn’t work with newer PHP versions, ALT‑PHP is a better option. It lets you safely run outdated PHP versions with CloudLinux security patches.
How to Use ALT‑PHP via PHP Selector
By default, cPanel uses EA‑PHP (EasyApache PHP) for all domains. That means when you first log into your account, your website is likely running an ea‑php version like ea-php74 or ea-php81. Because of this, the “Use PHP Selector” button in cPanel will appear disabled or unclickable.

To start using ALT‑PHP and unlock the PHP Selector tool, you need to switch your domain to an ALT‑PHP version first. Here’s how:
-
Go to MultiPHP Manager in your cPanel account (under the Software section).

-
Find your domain name in the list.
-
From the version dropdown, select an ALT‑PHP version (such as alt-php74 , alt-php80, etc.).
-
Click Apply to save the change.
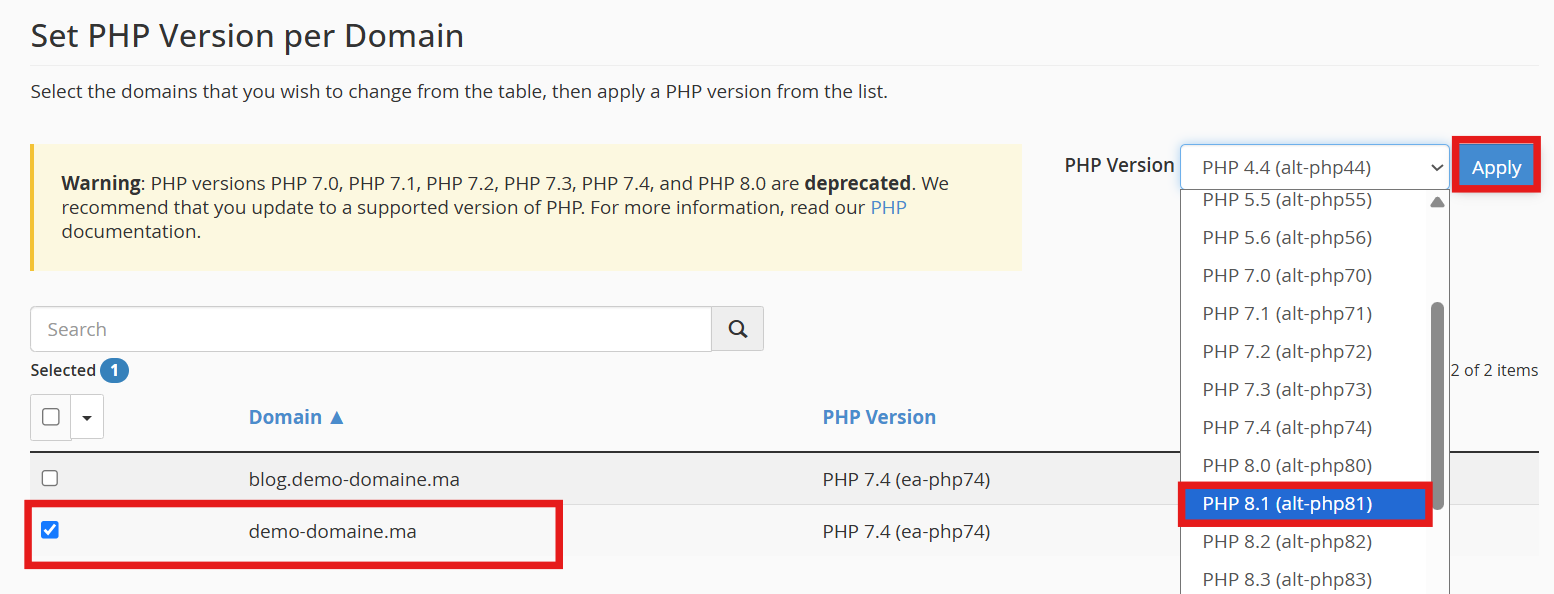
Once your domain is set to use an ALT‑PHP version, return to Select PHP Version in cPanel. The PHP Selector will now be active and usable.
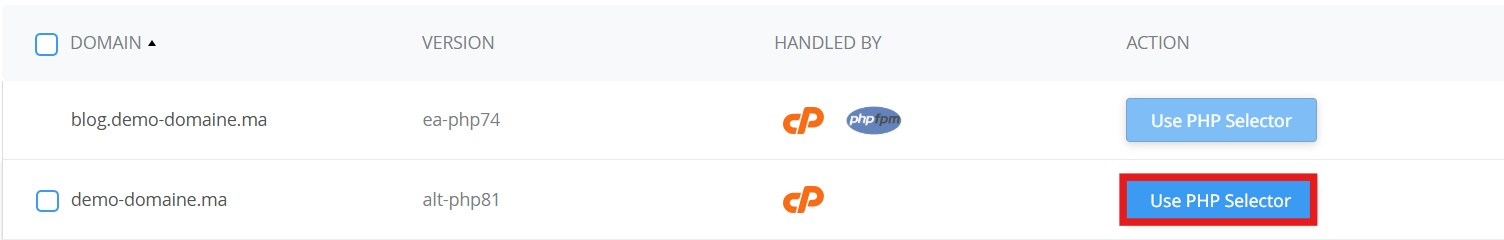
Once you click on Use PHP Selector, a pop up will appear asking you to confirm your choice
click on Confirm and the selected domain will be then managed under PHP Selector

From there, you can:
-
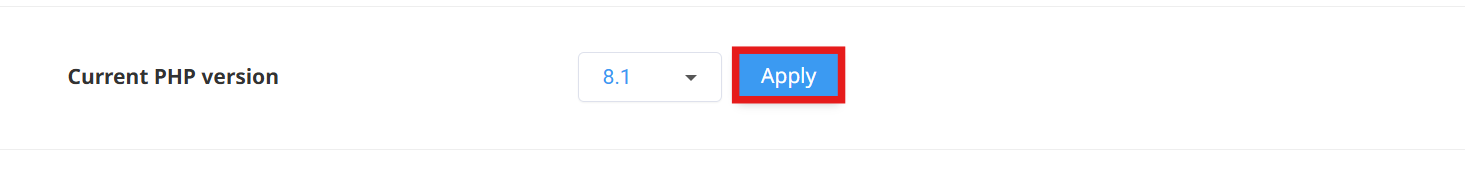
Change the PHP version to another ALT‑PHP release.
-
Enable or disable PHP extensions.
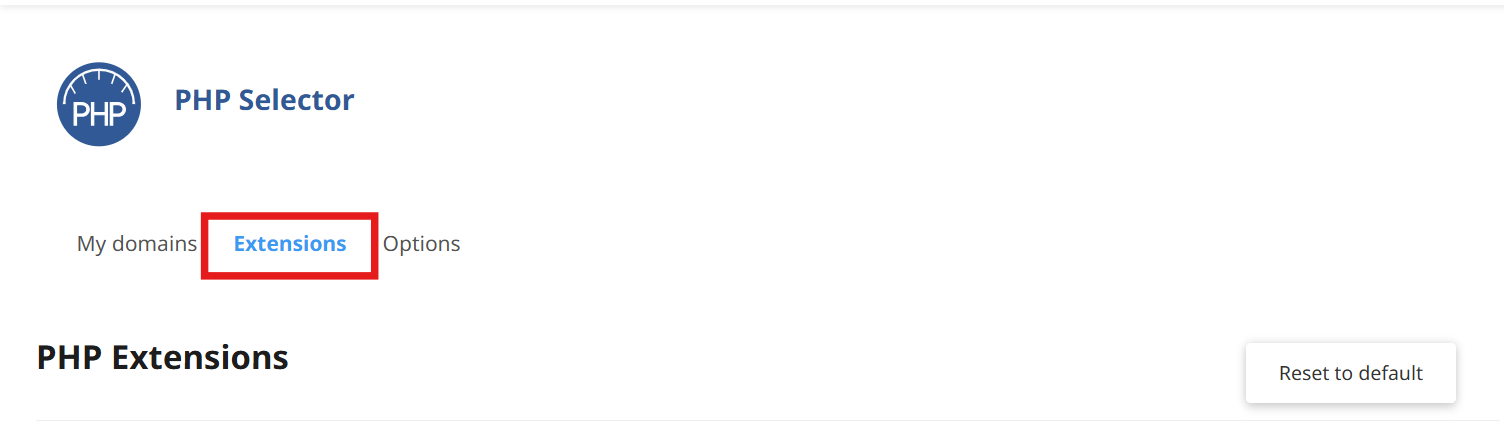
This gives you full control over your PHP settings
Depending on your hosting provider’s setup, you may only have one of these systems available. If you’re unsure, ask your hosting provider or system administrator.
Summary
- Use EA‑PHP for modern websites with official PHP support and full cPanel integration.
- Use ALT‑PHP for older apps that need legacy versions and user-level configuration.
- ALT‑PHP is managed through PHP Selector, while EA‑PHP is controlled via MultiPHP Manager.